Brew list ansible Error: No such keg: /usr/local/Cellar/ansible. I’m not really sure what happened. I’ve got the Ansible scripts in my path, but I don’t have the python modules. I prefer to install Ansible via pip so I simply pip install ansible and everything was right with the world. An icon used to represent a menu that can be toggled by interacting with this icon.
You can install Ansible quickly in your system with Homebrew( or PIP(Package manager for Python)

Install Ansible with Homebrew
If you are using macOS, then you can use Homebrew.
First, ensure that you have Homebrew installed in your system. Homebrew is a package manager for Mac OS. So if you want to learn more details about it, visit my blog below.
Run the following commands in your terminal. But, just copy commands without $ sign.
Checking Ansible version
Install Ansible with PIP
Ensure that you have Python and PIP in your system. Check the following page about Python installation.
Updating Ansible
Installing specific Ansible version
-->This quickstart shows how to install Ansible using the Azure CLI.
In this quickstart, you'll complete these tasks:
- Create an SSH key pair
- Create a resource group
- Create a CentOS virtual machine
- Install Ansible on the virtual machine
- Connect to the virtual machine via SSH
- Configure Ansible on the virtual machine
Prerequisites
- Azure subscription: If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
- Azure service principal: Create a service principal, making note of the following values: appId, displayName, password, and tenant.
- Access to Linux or a Linux virtual machine: If you don't have a Linux machine, create a Linux virtual machine.


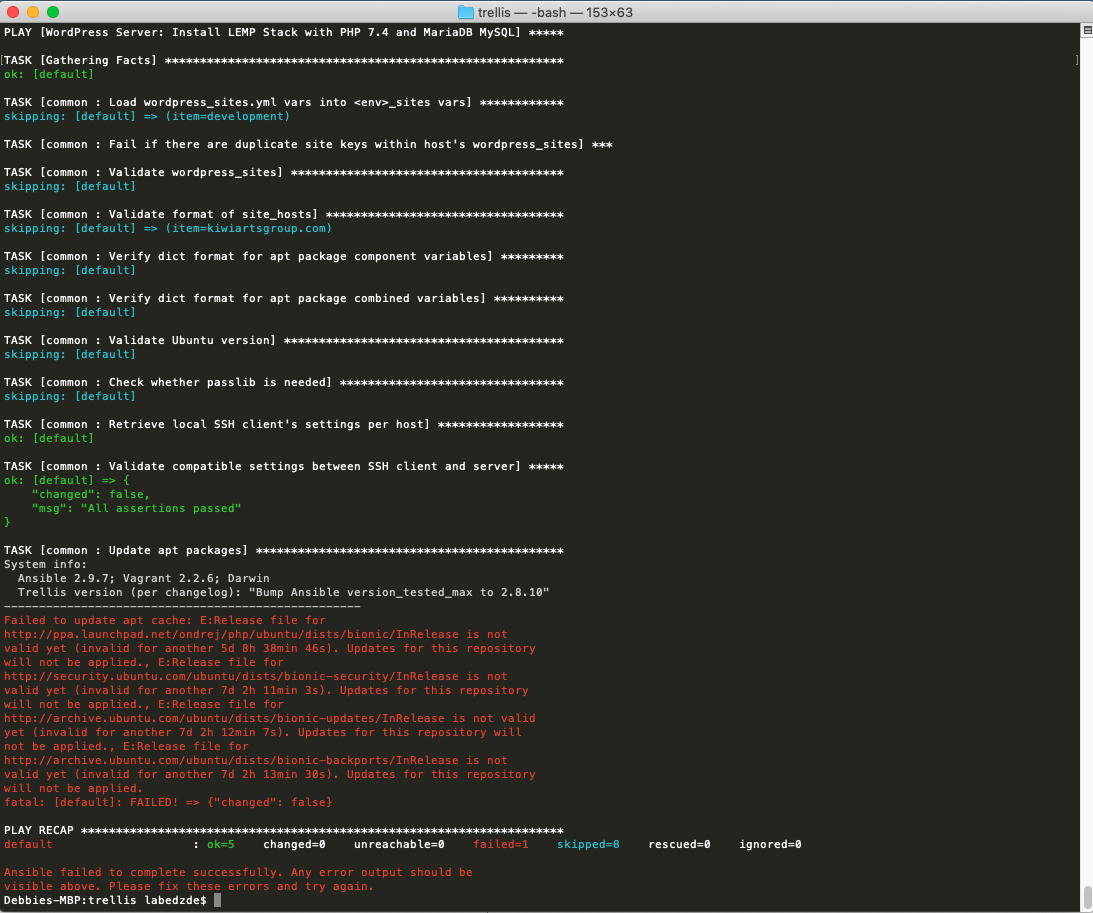
Brew Ansible-playbook
Create an SSH key pair
When connecting to Linux VMs, you can use password authentication or key-based authentication. Key-based authentication is more secure than using passwords. As such, this article uses key-based authentication.
With key-based authentication, there are two keys:
- Public key: The public key is stored on the host - such as on your VM (as in this article)
- Private key: The private key enables you to securely connect to your host. The private key is effectively your password and should be protected as such.
The following steps walk you through creating an SSH key pair.
Brew Ansible Command Not Found
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Open Azure Cloud Shell and - if not done already - switch to Bash.
Create an SSH key using ssh-keygen.
NOTE:
- The
ssh-keygencommand displays the location of the generated key files. You need this directory name when you create the virtual machine. - The public key is stored in
ansible_rsa.puband the private key is stored inansible_rsa.
Brew Ansible Pro
Create a virtual machine
Create a resource group using az group create. You might need to replace the
--locationparameter with the appropriate value for your environment.Create a virtual machine using az vm create. Replace the placeholder with the fully qualified name of your SSH public key filename.
Verify the creation (and state) of the new virtual machine using az vm list.
NOTE:
- The output from the
az vm listcommand includes the public IP address used to connect via SSH to the virtual machine.
Connect to your virtual machine via SSH
Using the SSH command, connect to your virtual machine's public IP address.
Replace the placeholders with the appropriate values returned in pervious commands.
Brew Ansible Tutorial
Install Ansible on the virtual machine
Run the following commands to configure Ansible on Centos:
Create Azure credentials

To configure the Ansible credentials, you need the following information:
- Your Azure subscription ID and tenant ID
- The service principal applicationID, and secret
Configure the Ansible credentials using one of the following techniques:
Option 1: Create Ansible credentials file
In this section, you create a local credentials file to provide credentials to Ansible. For security reasons, credential files should only be used in development environments.
For more information about defining Ansible credentials, see Providing Credentials to Azure Modules.
Once you've successfully connected to the host virtual machine, create and open a file named
credentials:Insert the following lines into the file. Replace the placeholders with the service principal values.
Save and close the file.
Option 2: Define Ansible environment variables
On the host virtual machine, export the service principal values to configure your Ansible credentials.
Test Ansible installation
You now have a virtual machine with Ansible installed and configured!
This section shows how to create a test resource group within your new Ansible configuration. If you don't need to do that, you can skip this section.
Create an Azure resource group
Save the following code as
create_rg.yml. Pgp for mac.Run the playbook using ansible-playbook. Replace the placeholders with the name and location of the resource group to be created.
Notes:
- Due to the
registervariable anddebugsection of the playbook, the results display when the command finishes.
- Due to the
Delete an Azure resource group
Save the following code as
delete_rg.yml.Run the playbook using the ansible-playbook command. Replace the placeholder with the name of the resource group to be deleted. All resources within the resource group will be deleted.
Notes:
- Due to the
registervariable anddebugsection of the playbook, the results display when the command finishes.
- Due to the
Brew Ansible
Run az group delete to delete the resource group. All resources within the resource group will be deleted.
Verify that the resource group was deleted by using az group show.
Run Remove-AzResourceGroup to delete the resource group. All resources within the resource group will be deleted.
Verify that the resource group was deleted by using Get-AzResourceGroup.
Homebrew Cask Install
Next steps
